Spectrometer
Spectrometer is an Instrument used to measure / Analyze the light over a specific portion of Electromagnetic Spectrum. Spectrometer is an optical instrument that can detect spectral lines and measure their wavelength or intensity.
What is Atomic Emission Spectrometry?
Atomic emission spectroscopy (AES) is a method of chemical analysis that uses the intensity of light emitted from a flame, plasma, arc, or spark at a particular wavelength to determine the quantity of an element in a sample.
What is Optical Emission Spectrometry?
Optical emission spectrometry (OES) is an analytical technique, universally considered and used to determine the chemical composition of metal alloys.
Above both are meaning the same.
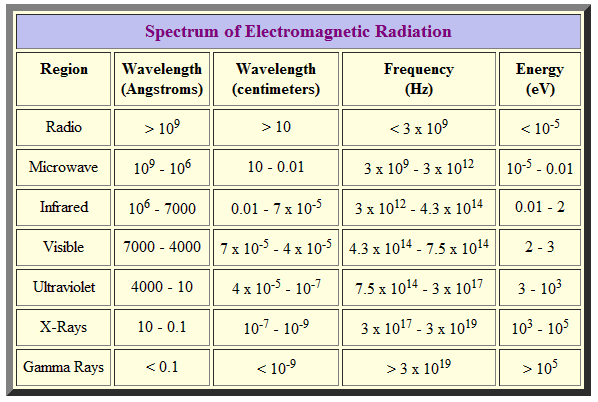
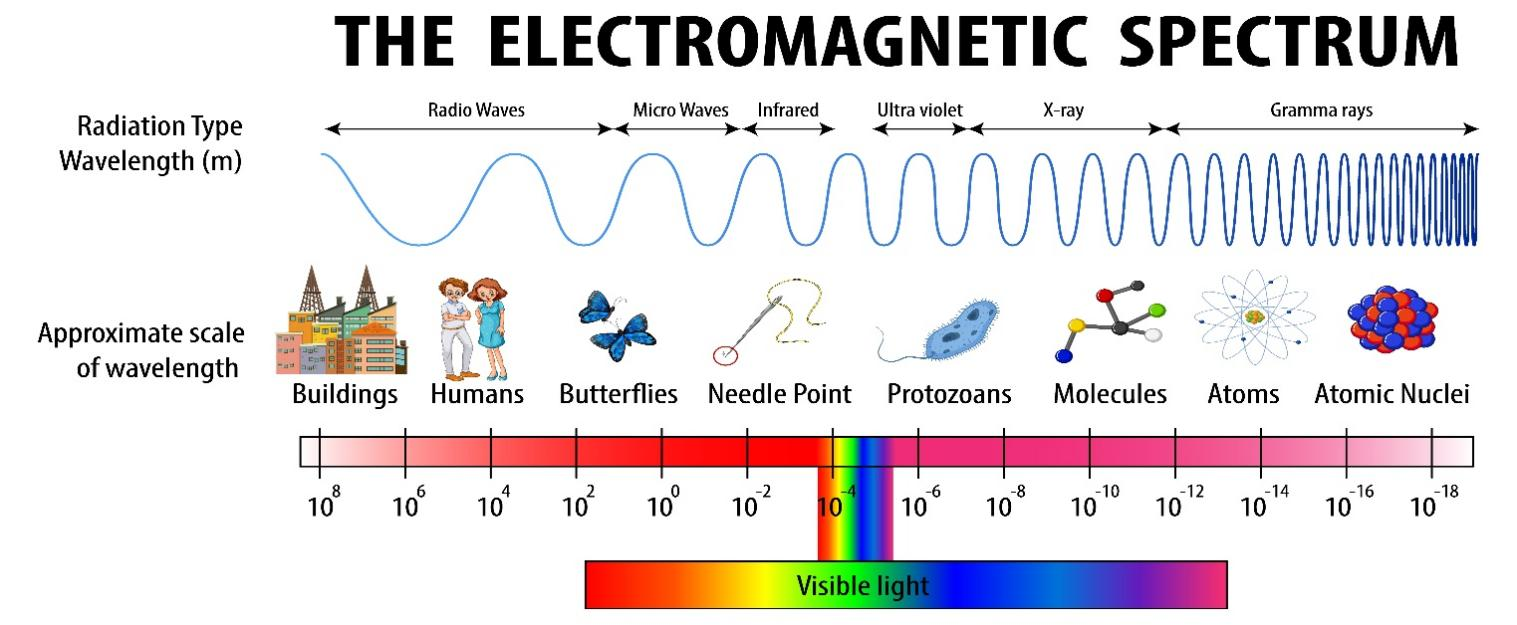
Electromagnetic Spectrum
The Electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all possible frequencies of Electromagnetic Radiation. Electromagnetic waves are typically described by any of the following three physical properties: the frequency f, wavelength λ, or photon energy E.
Wavelength is inversely proportional to the wave frequency, so gamma rays have very short wavelengths that are fractions of the size of atoms, whereas wavelengths on the opposite end of the spectrum can be as long as the universe.
Photon energy is directly proportional to the wave frequency, so gamma ray photons have the highest energy (around a billion electron volts), while radio wave photons have very low energy (around a femtoelectronvolt). These relations are illustrated by the following equations:
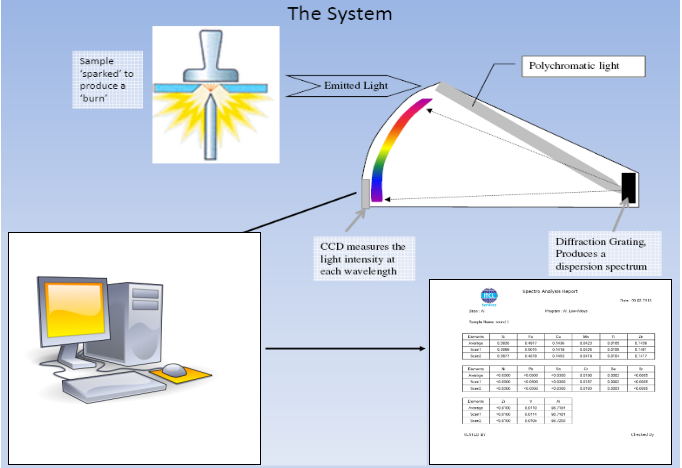
The Optical Emission Spectrometer
Generates the above light Spectrum from the sample and analyses and give the elemental concentration of the sample.
You all will be very eager to know
How the Light is generated from the Sample?
For this we must all go back to our school general physics and chemistry.
- What are Atoms?
- Atomic Structure of an Atom.
- Basic Atomic Theory?
- Ground State of Atom, Excited State of Atom
- Flame Test for Element Analysis.
General Physics
What are Atoms?
Atoms are the basic building blocks of ordinary matter. Atoms can join together to form molecules, which in turn form most of the objects around you.
Atoms are composed of particles called protons, electrons and neutrons.
Protons carry a positive electrical charge,
Electrons carry a negative electrical charge and
Neutrons carry no electrical charge at all.
The protons and neutrons cluster together in the central part of the atom called the nucleus, and the electrons ‘orbit’ the nucleus.
Atomic Structure
Different element depending upon to their Atomic Number has its own Atomic Structure. Below are atomic structure of Si, Cu and Fe.

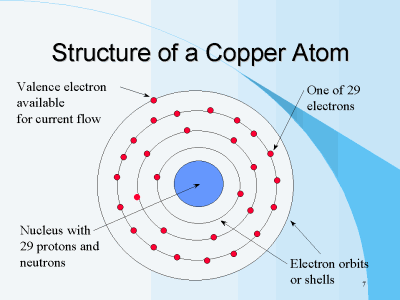
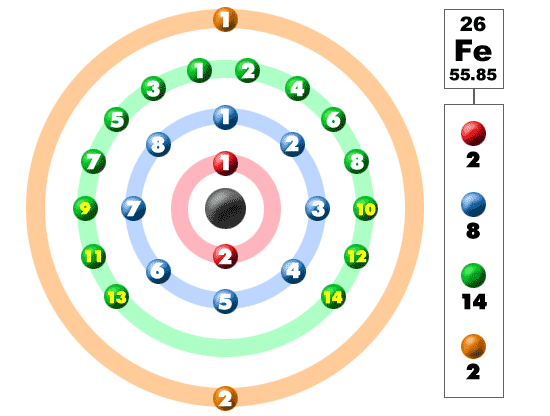
All the elements in the periodic table depending to its Atomic Number it has its own Atomic structure.
Ground vs. Excited State
Ground State – electrons are in positions of lowest energy possible (normal)


Excited State – electron is in a temporary position of higher energy than ground state. Very unstable; the electron quickly returns to the ground state

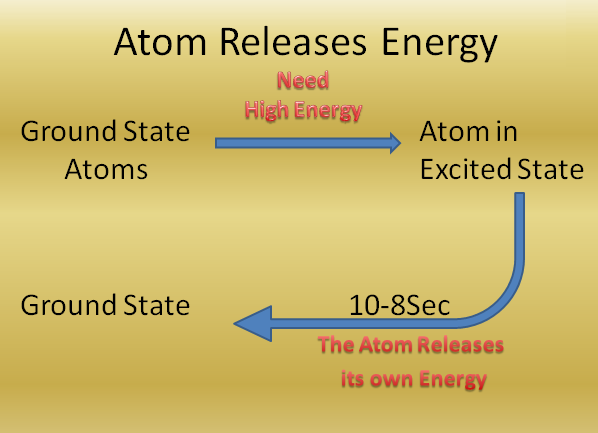
An atom in an excited state normally remains in that state for a very short time
(about 10-8 sec)
In Simple
Any Atom is normally in Ground State by applying High Energy the Atoms are taken to the unstable state called Excited State.
Need
High Energy
Ground State
Excited State
An atom in an excited state normally remains in that state for a very short time (about 10-8 sec). It will try to come back to the original state / ground state.
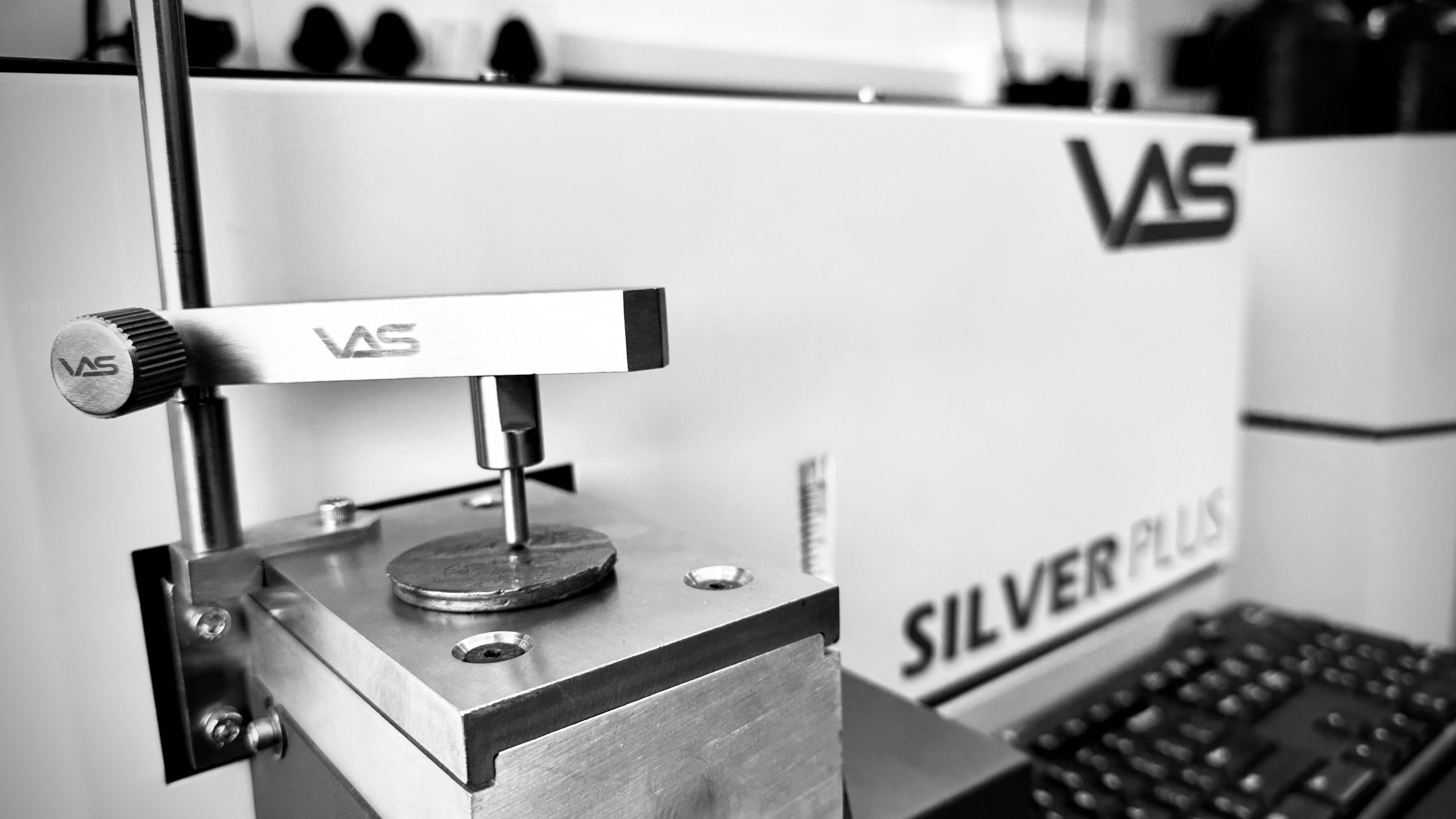
Principle of Operation of Optical Emission Spectrometer
The Optical Emission Spectrometer has two major components
- Spark Chamber
- Optics Chamber
SPARK CHAMBER
The Chamber used to generate the Source of Light /Electromagnetic radiation from the Sample which need to be analyzed.
Sample Excitation
In Spark Chamber the Samples are excited i.e. all the atoms in the samples are getting excited.
For Example, an Aluminum Alloy sample consist of all the following (Si, Fe, Cu, Mg, Mn, Zn) major, (Ni, Ti, Pb, Sn) minor and some trace elements are being excited.
Flame Test:
In Spark Chamber the Samples are excited i.e. all the atoms in the samples are getting excited.
For Example, an Aluminum Alloy sample consist of all the following (Si, Fe, Cu, Mg, Mn, Zn) major, (Ni, Ti, Pb, Sn) minor and some trace elements are being excited.

All the elements in the sample above are excited simultaneously release its own light energy (Color). Each and every element has its own light which is termed as wavelength (λ)
THUS SOURCE OF LIGHT IS GENERATED THROUGH SPARK CHAMBER
As said above all the elements releases light energy simultaneously. These all light emitted from the sample mix/combine produces a white composite light.
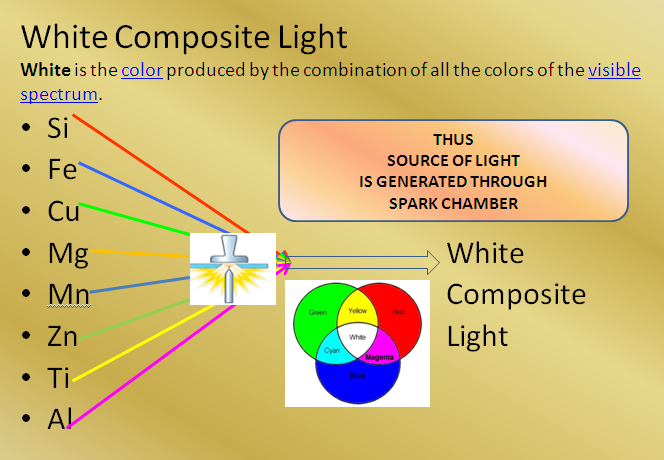
The light generated from Spark Chamber now needs to be separated for getting the individual concentration of each element in the sample for which you need a separate chamber called OPTICS CHAMBER.
OPTICS CHAMBER
Optics Chamber Analyzes the light generated from Spark Chamber and gives the exact elemental concentration of the sample.
White composite Light generated through Spark Chamber is made to pass through Optics Chamber for analyzing the Elemental Concentration of the Sample. White Light is Mixture of all Element light of the Sample.
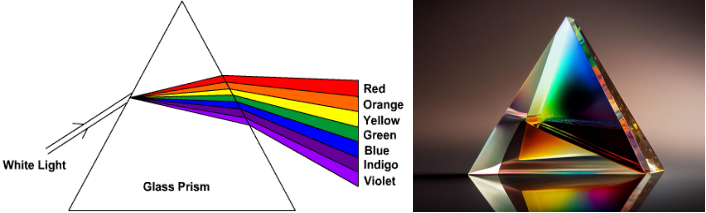
OPTICS CHAMBER DOES THE ABOVE JOB
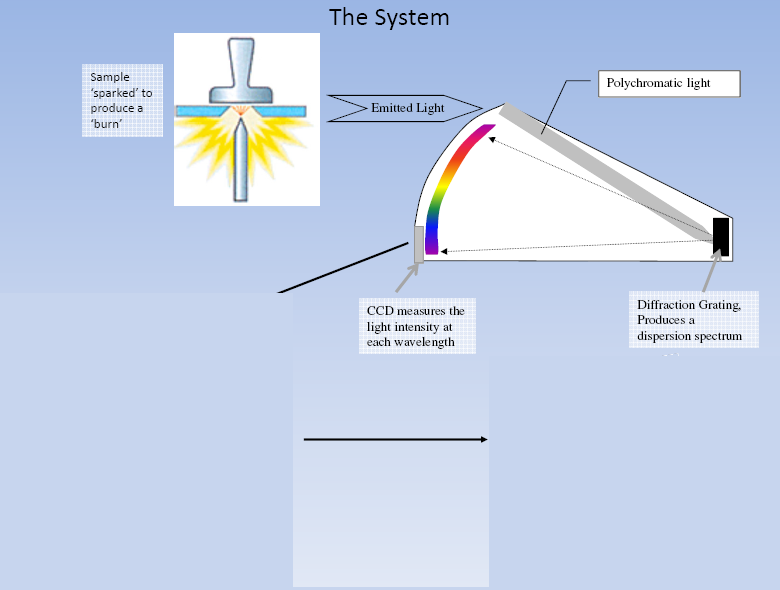
Optics Chamber in our spectrometer uses Diffractions Grating. It is modern technology device which replaces the prism for light/line separation. Diffraction grating has up to 4000 rules/mm. The white composite light is sampled using entrance slit and made to fall on diffraction grating.
The White light is reflected and diffracted producing a light spectrum. The Diffracted light is then focused to the detector. The detector here is CCD (Charged Coupled Device) simultaneously detect all incident light and determine the intensity of each wavelength.
Optics Chamber Schematic
The Photograph that we take through CCD is

Complete System